Introduction
Throughout its history, dentistry has experienced notable
progress, transitioning from a concept based on functional and
biological aspects to a modern evolution focused more on the
patient, particularly their aesthetic concerns. Indeed, the smile
constitutes the essence of social interactions, and depending
on societies and cultures, it can be associated with intelligence,
social status, confidence, and happiness [1,2].
Visible differences in dental appearance, such as enamel
opacities, can have a considerable psychosocial impact on individuals, especially adolescents who are developing their sense
of self, forming relationships, and striving to find their place in
society [2,3].
These opacities represent a quality defect in the enamel, visually identified as a variable-sized whitish spot. From a histological perspective, it is characterized as enamel hypomineralization, where the organic phase outweighs the mineral phase,
resulting in porous and permeable enamel [4,5]. Numerous factors can contribute to these lesions, such as prolonged plaque
accumulation on the affected tooth surface, dental fluorosis,
trauma, or molar incisor hypomineralization (MIH) [5,6]. However, these discolorations may appear similar since they result
from the same mechanism of action. Yet, in each case, hypomineralization takes on distinct topographic forms, which affect treatment decision and prognosis. Hence, the importance
of meticulous clinical observation of the lesions and the use of
specific tools like transillumination [6-9] to implement targeted
therapeutic approach.
In this context, a range of options is available to treat these
white lesions, the choice relies on the precise diagnosis of lesion location, depth, histopathological characteristics, and patient’s age [3,4,7].
The aim of our article is to describe the aesthetic management of white spots on anterior teeth affected by MIH using the
technique of deep infiltration. Emphasis will be placed on the
essential characteristics of enamel lesions that guide diagnosis
and treatment, as well as the key points for the success of this
therapeutic approach.
Clinical case
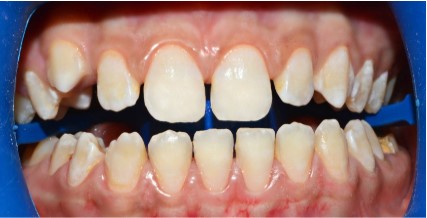
A 14-year-old patient, in good general health, presents with
an aesthetic discomfort related to white spots on his upper and
lower anterior teeth.
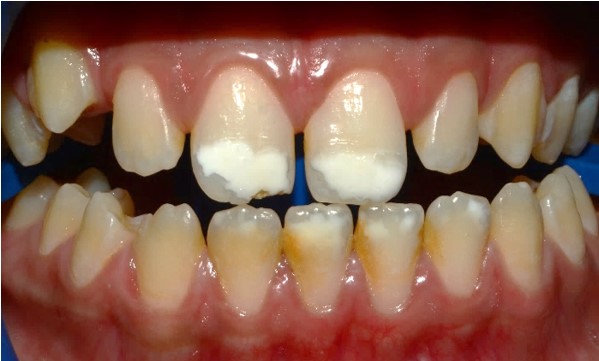
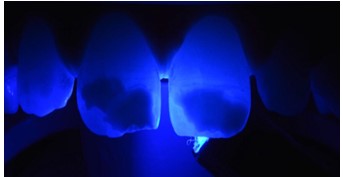
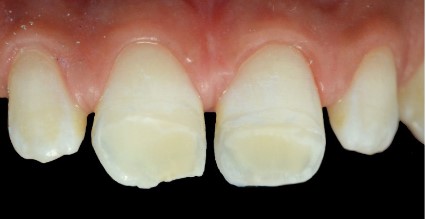
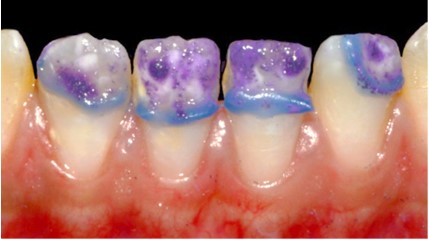
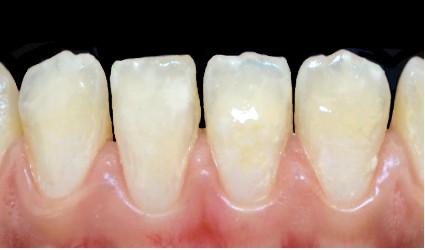
Upon clinical examination, whitish spots are observed at the
incisal third of the maxillary central incisors and the four mandibular incisors, along with dental plaque and tartar around the
mandibular anterior teeth (Figure 1).
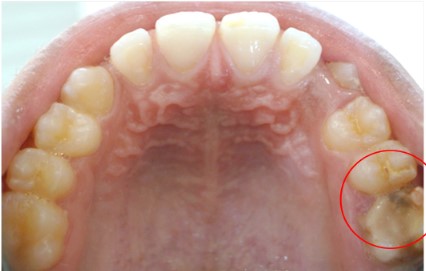
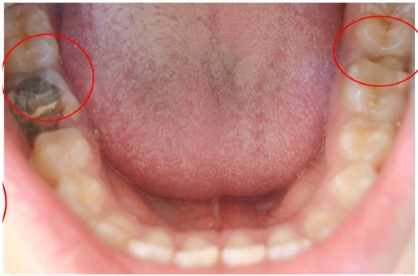
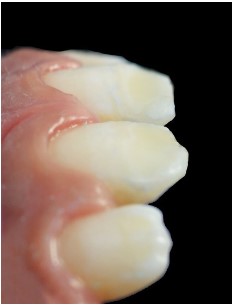
When examining the posterior teeth, carious substance loss
is noted on tooth 26, a large amalgam restoration on tooth 46,
and a fractured occluso-distal composite resin restoration on
tooth 36 (Figures 2,3). Based on this clinical examination, we
can deduce that the patient presents “Molar Incisor Hypomineralization (MIH)”.
- Diagnosis of enamel opacities :
Upper incisors:
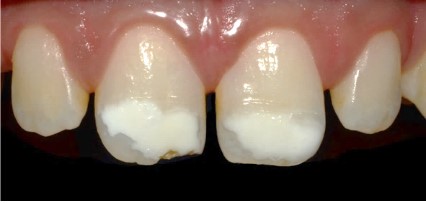
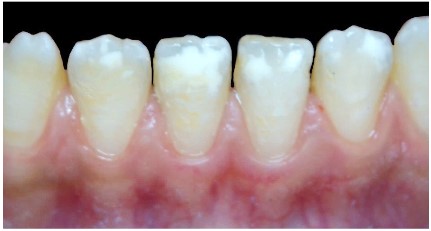
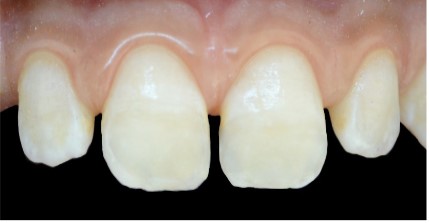
▪ Visual examination reveals five essential characteristics of these lesions (Figure 4):
1. Location: The opacities are in the incisal third of the
teeth, occupying almost half of the coronal height.
2. Color: In tooth 11 the opacities appear white, with a
yellowish zone at the incisal edge (area of substance loss). In
tooth 21, the opacity is white with a yellowish zone in the center.
3. Surface condition: The surface of tooth 21 is smooth,
while tooth 11 has mostly a smooth surface, except at the incisal edge where the surface is rough due to enamel breakdown.
4. Opacity: The opacities are opaque, indicating a loss of
translucency in the affected enamel.
5. Contour: The contour of the opacities is irregular, suggesting an uneven and non-uniform appearance.
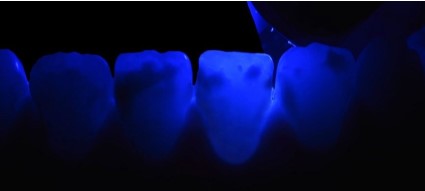
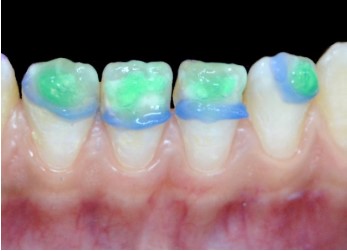
▪ Transillumination
Tooth 11:The lesion appears very dense with a mostly well-defined contour, blurred in its mesial part with substance loss.
Tooth 21: The lesion is dense in the distal part, and the rest
appears blurry with poorly defined contour (Figure 5).
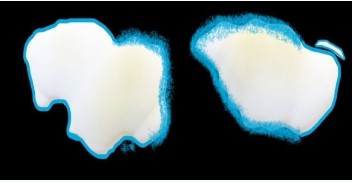
▪ Topographic mapping of the lesion
Creating a schematic representation of the shape, color, and
contour of the lesions, which guide the diagnosis and treatment
approach (Figure 6).
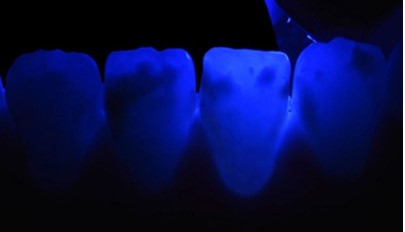
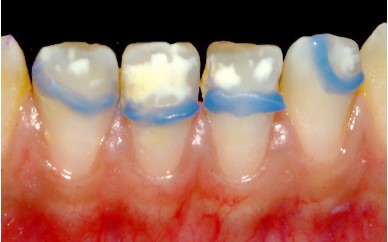
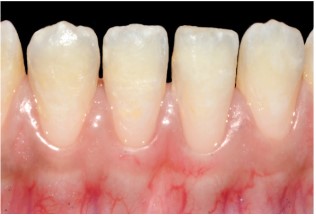
Lower incisors:
The spots are in the incisal third, appearing white with a
smooth surface, opaque, and an irregular contour (Figure 7).
Transillumination reveals a blurry appearance of the lesions
(Figure 8).
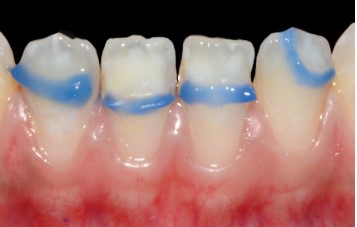
▪ Treatment: Deep Infiltration
Upper incisors
Discussion
Definition
The term Molar-Incisor Hypomineralization (MIH) was first
introduced in 2001 by "Weerheijm and al" to describe a systemic
origin hypomineralization with qualitative defects of enamel that occur asymmetrically on one or more of the permanent first molars, with or without involvement of the incisors
[6,10,11,12].
Prevalence
A recent systematic review and meta-analysis conducted by
"Schwendicke and al. 2018" estimated a global average prevalence of MIH at 12.9% (11.7-14.3%), with significant variations
between countries. Another meta-analysis by "Zhao and al. 2018"
estimated the prevalence of MIH to be around 14%, with no statistically significant difference between sexes, and it was found
to be more frequent in patients under 10 years of age (15%)
[13,14].
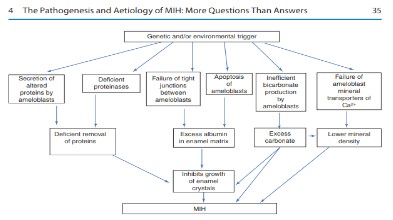
Etiology
Regarding the etiology of MIH, researchers have not yet
reached a clear consensus. Most of the factors that have been
implicated so far include childhood illnesses, medications taken
during amelogenesis (such as antibiotics), environmental toxins, fever, asthma, and pneumonia [13,15,16].
Diagnosis of MIH
Historically, a variety of terms and definitions have been used to
describe different enamel developmental defects. Regarding MIH,
a set of diagnostic criteria has been established by Weerheijm and al.
[11], three of which were diagnosed in our clinical case:
Table 1: Diagnostic criteria of MIH.
| Demarcated opacities |
– Clearly demarcated opacities
– Variability in color and size |
| Posteruptive enamel
breakdown |
Surface defect or enamel loss on a surface that
was initially formed after tooth eruption: on
tooth 26 and on the incisal edge of the 11 (mesial
angle). |
| Atypical restorations |
Large amalgam restoration on tooth 46 and a
fractured occluso-distal resin composite restoration on tooth 36. |
| Extraction of molars due to MIH |
Not diagnosed in our case. |
| Failure of eruption of a molar or an incisor |
Differential diagnosis
Clinically, MIH can be confused with other structural anomalies.
It is essential to understand the specific characteristics of each lesion to differentiate them and guide the treatment plan.
Table 2: MIH Differential Diagnosis
| Amelogenesis
Imperfecta (AI) |
Due to the diverse clinical presentations of AI, some cases may be challenging to distinguish from MIH. However,
the widespread involvement of primary and permanent
teeth and a common family history can help guide the
diagnosis toward a genetically based disorder. |
| Fluorosis |
The teeth are symmetrically affected and show linear
white, yellow, or brown opacities without clear boundaries in the enamel. In contrast, MIH does not exhibit
diffuse opacities but rather well-defined opacities. Anamnesis focused on fluoride history can also help distinguish fluorotic lesions from opaque MIH lesions. |
| Enamel Hypoplasia |
Clinically, hypoplasia can show a wide variation in the
number of affected teeth and is rarely of regular shape.
History of trauma or periapical inflammation of the primary tooth is most involved. The borders of hypoplastic
lesions are generally regular and smooth, indicating a
lack of enamel matrix formation during amelogenesis.
In contrast, the margins of lesions related to MIH are irregular. |
| White Spot Lesions |
They represent early sign of dental caries. They can be
seen because of prolonged plaque accumulation on the
affected tooth surfaces. These stains are distinguished
from MIH by their cervical or gingival location, which are
areas of plaque stagnation. |
Characteristics of dental enamel in the case of MIH
Unlike other white enamel lesions, MIH-related lesions extend
throughout the entire thickness of the enamel, starting at the
enamel-dentine junction and ending at the surface [6,18,19].
Various methods such as optical microscopy, polarized light microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and transmission electron
microscopy have been used to study the structural properties of
enamel affected by MIH [18,20]. These tools have shown:
- Significantly lower hardness and modulus of elasticity compared to sound enamel.
- Significant decrease in mineral density (approximately-20%).
- Significantly higher protein content.
- Increased porosity.
- Higher concentrations of carbon and carbonate.
- Thicker prism sheaths and higher inter- and intra-prismatic concentrations of organic particles [18,20].
Optically, the heterogeneity of the crystalline organization
contributes to the disruption of the trajectory of light rays, causing all incident light to be reflected from these lesions, resulting
in their whitish appearance [4].
As a result:
⮷ Enamel in teeth affected by MIH poorly support underlying restorations due to its low hardness and low elasticity
[18,20].
⮷ The bond between enamel and adhesive restorations
is often compromised due to an increased proportion of organic
matrix [18].
⮷ Acid etching prior to adhesive restorations, such as
composite, induces more pores and cracks compared to sound
enamel [18,21].
⮷ This histological structure implies weak mechanical
properties and explains the occurrence of cracks or fractures in
teeth affected by MIH, hypersensitivity in some cases, difficulties in anesthetizing affected teeth, and increased susceptibility
to carious lesions [12,10,22,10].
Diagnosis of white spots related to MIH
🡆 Visual examination
A thorough visual examination can allow us to read a "topographic mapping" of the lesion [7]. The teeth should be examined
while wet; however, if necessary, cotton rolls can be used to clean
the surface for better visualization of the lesions [11,13]. Some
white lesions are only slightly whiter than sound enamel, and air
drying may be necessary to detect them, while others are intensely
white and easily visible even on a wet tooth surface [7].
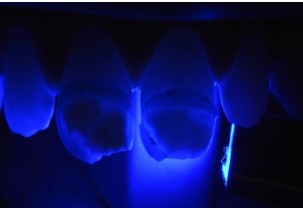
🡆 Transillumination
Sound enamel is translucent. It not only allows the passage
of light but also its dispersion. During transillumination, the
teeth are illuminated from their lingual surfaces, and the light
passes through the dental structure until it reaches the outer
tissue. Thus, opacity is decomposed based on the amount of
light that reaches the surface.
This simple, non-invasive, and painless method is useful for
mapping white enamel lesions in the anterior teeth. It increases the contrast between sound enamel and hypomineralized
enamel, allowing a better evaluation of the number of lesions,
their boundaries, and their depths [7,9,20].
Based on visual examination and transillumination, a new
topographic classification of white spots has been established
(WSTC) [4,7]:
Table 3: White spot topographic classification (WSTC).
| Superficial lesions |
Deep lesions |
Mixed lesions |
| Depending on the thickness of the lesion, the appearance may be: |
• The lesion is covered by
translucent sound enamel
that disperses light away
from the spot, which appears
blurred with poorly defined
boundaries.
• Creamy and yellowish appearance |
A portion of the lesion is
deep, while the other part is
superficial. |
| Thin superficial lesions |
Thick superficial lesions |
• Slightly whiter than sound enamel.
• Difficult to distinguish from underlying
enamel.
• Can only be detected after prolonged air
drying. |
• Much whiter compared to sound
enamel.
• Easy to distinguish from underlying
enamel.
• Visible even on a wet surface |
This classification has a purely therapeutic purpose as it
clinically guides us towards the appropriate treatment option
for each lesion based solely on its topography [7]. For our clinical case, based on this classification, we can conclude that the
white lesions associated with the upper incisors are mixed,
while those on the lower teeth are deep.
Treatment
In every aesthetic demand biological, biomechanical, functional, and aesthetic imperatives are inseparable, and the practitioner must choose a solution adapted to the clinical situation
from a range of treatments, from the most conservative to the
least conservative [23].
In the case of MIH, the enamel lesions have the particularity
of starting not in the subsurface, but at the amelodentinal junction. They have an internal location that is not easily reached
by the standard erosion protocol. Therefore, the principle of
treatment by deep erosion/infiltration of MIH is to remove the
ceiling of the lesion through sandblasting or milling before infiltration, followed by restoration with composite resin to ensure
satisfactory aesthetic results [8,24,25]. Indeed, this area cannot be reached during the successive stages of erosion (multiple applications of HCl), and infiltration may occur at the level of sound enamel, producing no favorable optical effect. That
is why treatments by erosion/infiltration of MIH lesions were
rarely successful [6,24]. However, the option of deep infiltration
can only be successful through the respect and understanding
of each step of the treatment and the knowledge of the mechanism of different products used.
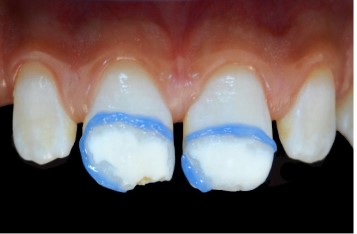
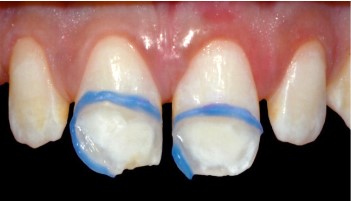
- Lesion isolation: Creates a barrier between sound enamel
and hypomineralized enamel and minimizes the waste of various products required for the abrasion-infiltration protocol.
After photopolymerization, this barrier should remain in place
throughout all treatment phases [26].
- Microabrasion: For an ultra-conservative approach, the removal of superficial enamel layers was attempted to expose the
lesions. A total of 10 cycles of microabrasion were performed,
reducing the enamel thickness by 25 to 200 μm, which proved
to be insufficient to reach the ceiling of the lesions [27].
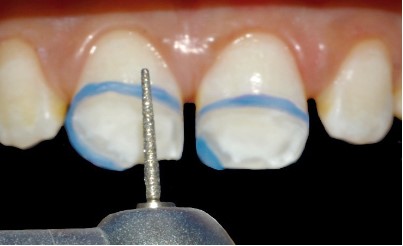
- Macroabrasion: Through milling, this approach is slightly
more invasive, but still limited to the enamel. The concept behind this technique is based on the removal of the superficial
layer of tissue recovering the white spot and transforming a
non-superficial enamel lesion into a superficial one which is exposed before its infiltration [3,13,24].
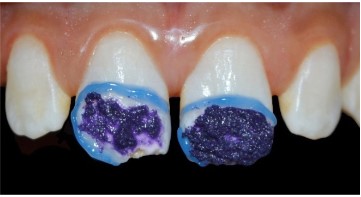
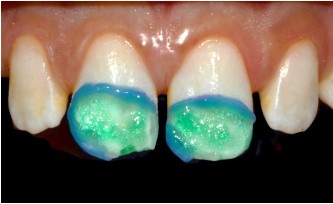
- Deproteinization: The purpose of deproteinization with
sodium hypochlorite is to remove organic barriers that hinder
infiltration. Hypomineralized enamel contains a significant protein component that limits resin infiltration. Sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) eliminates this protein component and increases
the porosity of hypomineralized enamel. This enhances the capillary effect underlying infiltration. Some authors recommend
rinsing the lesions with 5% sodium hypochlorite for 5 minutes.
In our clinical case, we opted for the use of sodium hypochlorite
gel (NaOCl gel), which provides better stability and maximum
contact with the tooth surface. Mechanical activation using a
microbrush for 60 seconds optimizes its effectiveness, allowing
targeted action limited to the affected enamel with less risk of
splashing [28,26].
- Substance loss control: Substance loss is ideally measured
using a thickness caliper. It indicates that the technique is minimally invasive and suggests the need for an additional restorative technique.
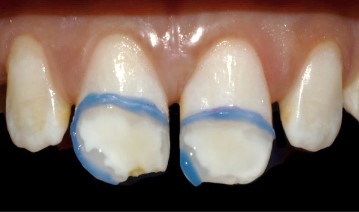
- Transillumination test: The removal of the enamel layer
covering the lesion is an essential prerequisite before any infiltration procedure. Transillumination, in addition to its diagnostic value, confirms the exposure of the bottom of the lesion
[26].
- Alcohol test: The main challenge of this therapeutic approach is knowing when to infiltrate the enamel opacity. Alcohol (ethanol) serves as an indicator of the position of the lesion's ceiling. With its relatively high refractive index, it shows
the result that will be obtained after resin infiltration. As soon
as the application of alcohol slightly masks the spot, it indicates
that we have reached the ceiling of the lesion and the infiltration will be sufficient to conceal it. If alcohol does not provide
this effect and the lesion remains white-opaque, it becomes
necessary to repeat one or two steps of chemical erosion (HCl)
because it has been reported that 29% of these opacities have
a thicker superficial enamel layer exceeding 50 μm, making it
difficult to create enough porosity with a single application of
15% HCl or, as in our case, further milling the enamel covering
the spots to reach the lesion's ceiling. In any case, infiltration
should never be performed if alcohol does not mask the lesion
[24,28,29].
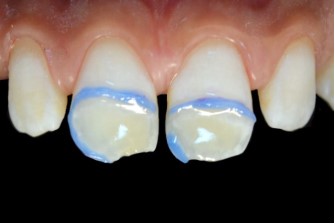
- Infiltration step: The main component of the infiltrating
resin is triethylene glycol dimethacrylate (TEGDMA), a low viscosity and highly fluid resin monomer with a refractive index
(1.52) close to that of sound enamel (1.62). It improves the
transmission of light photons through the hypomineralized
enamel and restores its translucent appearance [8,24]. In addition to its aesthetic properties, this resin increases the mechanical strength of demineralized enamel and makes it more
resistant to acid attack compared to sound enamel. This is due
to the ability of the resin infiltrant to impregnate the interprismatic enamel and form a reinforced resin-enamel tissue called
the hybrid layer, which is distinguished from dentin hybrid layers by the absence of collagen fibers [29,31]. However, the sealing properties of this product may be insufficient. It has been
reported that it can only seal about 60% of the enamel pore
volume, leaving a significant amount of untreated demineralized enamel. As a result, incomplete infiltration will result in
the persistence of an unaesthetic edge effect that can be easily
detected by transillumination. In this context, rehydration is of
crucial importance. Over time, the infiltrated lesion undergoes
water absorption, improving the translucency of the enamel (72
hours to one week) [4]. Recently, a new nano-structured resin infiltrant containing amorphous calcium phosphate nanoparticles (NACP) has been incorporated into ICON for the treatment
of white enamel lesions. The addition of 30% NACP to the ICON
resin has allowed for long-term release of Ca and P ions, acceptable biocompatibility, and the promotion of hardness and
mineral component deposition after a 14-day period [30].
- Composite resin restoration: MIH stains are not always
completely masked by resin infiltration alone. In certain situations, such as in our case, the use of composite resin above
the infiltrated areas is necessary to achieve an optimal result.
Placing composite resin without deep infiltration will result in
the inability to mask the lesion, a highly unsatisfactory aesthetic outcome, and insufficient application of the composite resin
due to the limited space unless the lesion is removed down to
the dentin, which goes against the principle of tissue preservation [3,13,27].
The choice of adding enamel or dentin composite depends
on the extent of substance loss: minimal loss, as in our clinical
case, requires the addition of enamel composite only, while in
the opposite case, both enamel and dentin composites are necessary to fill the area. Additionally, the composition of the resin
material is an important criterion, especially for anterior restorations. In our clinical case, a nanohybrid resin (Opallis) was
used, which has an average particle size of 0.5 μm. Compared
to microhybrid composite resins, "nanotechnology" has allowed the incorporation of new compounds with particle sizes
smaller than visible light wavelengths, thereby improving aesthetics, surface quality, and better light transmission through
the restoration. Moreover, these composites have shown good
resistance to wear, compression, and fractures, low polymerization shrinkage, ease of shaping, and quick polishing. Such differences should be taken into consideration to achieve aesthetic
restorations that closely resemble natural teeth [32,33].
Prognosis
The treatment of enamel opacities using the deep infiltration technique with ICON remains a highly conservative approach, ensuring a good long-term prognosis. However, many
authors have questioned the aging of the infiltrated resin, and
recent in vitro studies seem contradictory on this subject. Some
find that the infiltrated enamel shows stability for at least 6
months, while others believe that the demineralized infiltrated
tooth structure is more susceptible to external discoloration.
Indeed, through experimental studies, researchers have shown
that over time, black tea, black coffee, and red wine can alter
the hue of the infiltrated enamel [24,34,35]. Based on these
observations, some authors recommend ambulatory bleaching
for patients with discolored enamel lesions, even after resin infiltration treatment [34,35]. In this context, Rocha and al. (2020)
studied the limited effectiveness of bleaching on these lesions
and showed that the resin infiltrant acts as a semi-permeable
physical barrier to the bleaching agent, reducing the permeability of the enamel surface and decreasing the number of free
radicals, which hinders the degradation of pigment molecules.
However, further studies are needed to detect such an influence and supplement the results of current research [36].
It is essential to note that the problem of discoloration of the
infiltrating resin primarily occurs in cases of superficial infiltration because, in deep infiltration, such as in our clinical situation, the infiltrating resin is not in contact with the external environment, except through its adhesive seal, and is covered by
composite resin, which, in turn, may require maintenance and replacement over time. Indeed, composite restorations have a
limited lifespan, and marginal stains, wear, and fractures may
occur. Long-term maintenance is therefore essential for the success of the treatment [24,13,27].
Role of external bleaching in the management of MIH-related
enamel lesions
The color of hypomineralized enamel in cases of MIH can
range from white to yellow or brown. In the case of colored
stains, whether they are superficial or deep, resin infiltration
may prove ineffective. Indeed, during the infiltration of the lesion, a distinct color resurgence appears, and the treated areas may appear more yellowish. In the case of superficial infiltration, the failure is immediate, and even in cases of deep
infiltration, it will be challenging to hide this discoloration with
composite. Ideally, the colored stain should be transformed into
a whitish stain through prior tooth whitening, followed by infiltration. It may happen that the whitening alone is sufficient by
reducing the contrast between the tooth color and the lesion
and the patient is satisfied with the result.
After tooth whitening, a period of at least 15 days before
infiltration is essential. Indeed, the physical and chemical alterations that may occur in the enamel immediately after the
whitening procedure can lead to a loss of resin adhesion to the
enamel. Additionally, the presence of residual oxygen in the
whitened enamel hinders the resin polymerization process.
Color stability and normal bond strength are achieved within
three weeks following the whitening procedure [24,37,38].
Conclusion
So far, there is no minimally invasive aesthetic solution available to effectively treat enamel opacities related to MIH. In
some cases, a combination of multiple therapeutic protocols
may be necessary to meet the aesthetic needs of patients.
The concept of deep infiltration involves a slight removal of
sound enamel to reach the ceiling of the lesion, but it remains
within the thickness of the enamel. This approach aims to preserve maximum tooth structure and avoid more invasive treatments.
However, it is important to note that further clinical experience and long-term studies are needed to fully understand the
effectiveness and role of this therapy in daily practice.
References
- Pernilla Larsson, Lars Bondemark, Birgitta Häggman-Henrikson.
The impact of oro-facial appearance on oral health-related quality of life: A systematic review. J Oral Rehabil. 2020; 00: 1–11.
- Noren Hasmun, Mario V Vettore, Jennifer A Lawson, Claire Elcock, HallaZaitoun, Helen D Rodd Determinants of children’s
oral health-related quality of life following aesthetic treatment
of enamel opacities. J Dent. 2020; 98: 103372.
- Lygidakis NA, Garot E, Somani C, Taylor GD, Rouas P, et al. Best
clinical practice guidance for clinicians dealing with children presenting with molar incisor hypomineralisation (MIH): an updated European Academy of Paediatric Dentistry policy document.
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry. 2022; 23: 3–21.
- Marouane O, Douki N. Démarche diagnostique et thérapeutique
pour la gestion des taches blanches de l’émail researchgate.
333671242 June 2019.
- Koch G. An Introduction Molar Incisor Hypomineralization A
Clinical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment. 2019.
- Sampson V, Sampson A. Diagnosis and treatment options for anterior white spot lesions. British dental journal. 2020; 229.
- Chtioui F, Marouane O, Douki N. White Spot Lesions (Part I): A
New Topographic Classification (WSTC) Dental News, Volume
XXIV, Number IV, 2017.
- Júlia De Oliveira Farias, Maria Catarina Alves Cunha, Vivian Leite
Martins, Paula Mathias Microinvasive esthetic approach for
deep enamel white spot lesion. Dent Res J. 2022; 19: 29.
- Marouane O. The use of transillumination in detecting subclinical extensions of enamel opacities. J EsthetRestor Dent. 2019;
1–6.
- Kisby L. Resin Infiltration in the Treatment of MIH Lesions in Anterior Teeth in Pediatric Patients. DMGAmericaArticles_Ebooks.
2022; 12: 14.
- Katrin Bekes and Karin L. Weerheijm. Diagnosis, Classifications
and Treatment Strategies of MIH-Affected Teeth Molar Incisor
Hypomineralization A Clinical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment.
2019.
- Aghareed Ghanim, Rodrigo Mariño, David J. Manton. Validity
and reproducibility testing of the Molar Incisor Hypomineralisation (MIH) Index. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2018; 1–8.
- JoëlleA.Dulla Hendrik Meyer-Lückel. Molar-incisor hypomineralisation: narrative review on aetiology, epidemiology, diagnostics, and treatment decision, Swiss dental journal sso. 2021;
131: 11.
- Somani C, Taylor GD, Garot E, Rouas P, Lygidakis NA, Wong FSL.
An update of treatment modalities in children and adolescents
with teeth afected by molar incisor hypomineralisation (MIH):
a systematic review. European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.
2022; 23: 39–64.
- David J. Manton, Felicity A. Crombie, and Mihiri J. Silva. The
Pathogenesis and Aetiology of MIH: More Questions Than Answers Molar Incisor Hypomineralization A Clinical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment. 2019.
- Mihiri J Silva, Katrina J Scurrah. Etiology of molar incisor hypomineralization – A systematic review. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2016; 44; 342–353.
- A. Ghanim, MJ. Silva. Molar incisor hypomineralisation (MIH)
training manual for clinical field surveys and practice Eur Arch
Paediatr Dent. 2017; 18: 225–242.
- Karim Elhennawy, Katrin Bekes, Anton Dobsak, Stefan Tangl,
Hassan Shokoohi-Tabrizi, Falk Schwendicke Structural, Mechanical, and Chemical Evaluation of Molar Incisor Hypomineralization-Affected Enamel Molar Incisor Hypomineralization A Clinical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment. 2019.
- Karla Gambetta-Tessini, Rodrigo Mariño, Aghareed Ghanim,
Geoffrey G. Adams, David J. Manton. Validation of quantitative
light-induced fluorescence-digital in the quantification of demarcated hypomineralized lesions of enamel. J Invest Clin Dent.
2017; e12259.
- Omar Marouane, David J. Manton. The use of transillumination
in mapping demarcated enamel opacities in anterior teeth: A
cross-sectional study. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2022; 32; 49-55.
- Carola B. Bozal, Andrea Kaplan, Andrea Ortolani, Silvina G.
Cortese, Ana M. Biondi Ultrastructure of the surface of dental
enamel with molar incisor hypomineralization (MIH) with and
without acid etching. Acta Odontol. Latinoam. 2015; 28: 192-198.
- O. Marouane, N. Douki, F. Chtioui. A Combined Approach for the
Aesthetic Management of Stained Enamel Opacities: External
Bleaching Followed by Resin Infiltration Case Reports in Dentistry. 2018.
- Gil Tirlet et Jean Pierre Attal. Le Gradient thérapeutique un concept médical pour les traitements esthétiques L’information
dentaire n° 41/42 – 25. 2009.
- Jean-Pierre ATTAL, Anthony ATLAN, Maud DENIS, Elsa VENNAT,
Gilles TIRLET White spots on enamel: Treatment protocol by superficial or deep infiltration (part2) International Orthodontics
2014; 12: 1-31.
- Jean-Pierre Attal, Antony Atlan Maud Denis, Elsa Vennat, Gil
Tirlet Nouveau concept pour le masquage des taches de l’émail
L’infiltration en profondeur - Partie III Traitement d’une MIH
sévère. L’information dentaire n° xxx - x mois. 2014.
- Marouane O, Douki N. Traitement focal de l’hypominéralisation
traumatique de l’émail L’Information dentaire. 2016; 98: 2-7.
- Tam CP, Manton DJ. Aesthetic Management of Molar Incisor
Hypomineralization: Staged Strategies for Affected Incisors. Molar Incisor Hypomineralization A Clinical Guide to Diagnosis and
Treatment. 2019.
- Marouane O, Manton DJ. The influence of lesion characteristics
on application time of an infiltrate applied to MIH lesions on
anterior teeth: An exploratory in vivo pilot study. Journal of Dentistry. 2021; 115: 103814.
- Jorge Perdig~ao. Resin infiltration of enamel white spot lesions:
An ultramorphological analysis. J EsthetRestor Dent. 2019; 1–8.
- Dai Z, Xie X. Novel nanostructured resin infiltrant containing
calcium phosphate nanoparticles to prevent enamel white spot
lesions. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials. 2022; 126: 104990.
- Ayad AH, Mustafa DS, Nour KA. Effect of remineralizing agents
and resin infiltration on resistance to demineralization of artificial enamel lesions. 2020; 66: 2763: 2771.
- D Angerame, M De Biasi. Do Nanofilled/Nanohybrid Composites Allow for Better Clinical Performance of Direct Restorations
Than Traditional Microhybrid Composites? A Systematic Review.
Operative Dentistry. 2018; 43-4, E191-E209.
- Perez MM, hita-iglesias C, Ghinea R, Yebra A, Pecho OE, et al.
Optical properties of supra-nano spherical filled resin composites compared to nanofilled, nano-hybrid and micro-hybrid composites Dental Materials. 2016; 35: 353–359.
- Alqahtani S, Abusaq A, Alghamdi M, Shokair N, Albounni R. Colour stability of resin infiltrated white spot lesion after exposure
to stain-causing drinks.
- Yeslam HE, AlZahrani SJ. Time-dependent effect of intense capsule coffee and bleaching on the color of resin infiltrated enamel
white spot lesions: an in vitro study. Peer J. 2022; 10: e14135.
- Rafael Santos Rochaa, MaurícioYugo de Souzaa, Laura Célia Fernandes Meirellesb Effectiveness of Home Bleaching Treatment
after Resin Infiltrant Application. Oral HealthPrev Dent. 2020;
18: 549–554.
- V Cavalli, AF Reis, M Giannini, GMB Ambrosano. The Effect of
Elapsed Time Following Bleaching on Enamel Bond Strength of
Resin Composite. OperativeDentistry, 2001, 26, 597-602.
- Topcu FT, Erdemir U, Ozel E, Tiryaki M, Oktay EA, et al. Influence
of Bleaching Regimen and Time Elapsed on Microtensile Bond
Strength of Resin Composite to Enamel. Contemporary Clinical
Dentistry. 2017; 8.